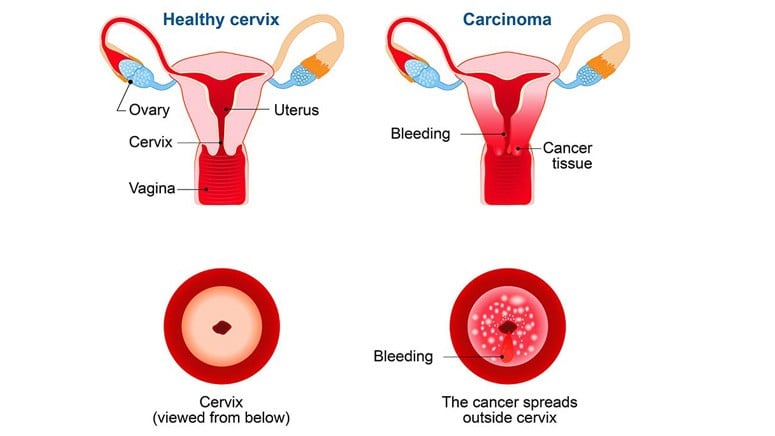
Cervical cancer is one of the different types of cancer, and this cancer starts at the cervix cells. The cervix is the lower part of the uterus that connects to the vagina in a woman. It occurs when there is an abnormal growth of cells known as dysplasia between the uterus and vagina (Cervix). Cancer does not just appear. It mainly develops after several years, usually as a result of an infection.
There are not many visible symptoms of cervical cancer, which makes it hard for women to detect or know if they have it. Cervical cancer is mostly seen in a pap smear when a gynecologist is examining one. If detected early, it can be treated accordingly before it causes significant problems and complications. Cervical cancer is an essential and critical health condition that was once a leading cause of death among women until it became widely available to undergo a screening test.
When rightly diagnosed, cervical cancer is one of the most successful treatable types of cancer. So far, it is noticed at the early stage and managed effectively. Since the symptoms are not too visible, it is hardly ever noticed on time. However, it can still be treated in its late stages, as long as you visit your doctor and undergo appropriate palliative care.
Causes of Cervical Cancer
 Cervical cancer starts when the healthy cervical cells develop some changes in their DNA. An alteration in a cell’s DNA can cause changes to the organ, and this is because a cell’s DNA is what instructs the cell on what to do. When the cells are healthy, they grow and multiply at a set rate, ensuring the body is in a healthy state. On the other hand, an abnormal change (mutation) in the DNA causes the cell to grow and multiply out of control. More abnormal cells are called a tumor. If Tumors are not treated immediately, they could spread to other areas of the body and cause more complications.
Cervical cancer starts when the healthy cervical cells develop some changes in their DNA. An alteration in a cell’s DNA can cause changes to the organ, and this is because a cell’s DNA is what instructs the cell on what to do. When the cells are healthy, they grow and multiply at a set rate, ensuring the body is in a healthy state. On the other hand, an abnormal change (mutation) in the DNA causes the cell to grow and multiply out of control. More abnormal cells are called a tumor. If Tumors are not treated immediately, they could spread to other areas of the body and cause more complications.
In the case of cervical cancer, the leading cause is sexually transmitted human papillomavirus (HPV). Human papillomavirus (HPV) is the same virus that causes genital warts. HPV contributes significantly to cervical cancer, although not all cases of HPV imply cervical cancer. The two types of HPV that cause cervical cancer are HPV-16 and HPV-18. It is also essential to know that even if you get infected with these types of HPV, it still doesn’t mean that you would contract cervical cancer; this is because your immune system does its job of fighting cancerous cells that tend to grow in the body. Also, scientists have proven that in most cases, the immune system is successful in eliminating the vast majority of HPV infections, often within two years.
HPV is a widespread infection and is also responsible for some other cancers in men and women. However, HPV may not be the only cause of cervical cancer or a factor contributing to cervical cancer. Your environment or your choice of lifestyle can also determine if you develop cervical cancer.