Breast cancer is a type of cancer that causes the cells in the breast to proliferate without control. There are several types of breast cancers. The type a person has depends on the type of breast cell it starts in. Most begin in the lobules or ducts [1].
This cancer affects both men and women, but the incidence is vastly higher in women. Due to advancements in medicine and increased awareness of the symptoms, mortality resulting from breast cancer has steadily declined. The symptoms of breast cancer differ from person to person and some may not experience symptoms at all. In many cases, the following symptoms may indicate breast cancer:
Lump in or around the breasts
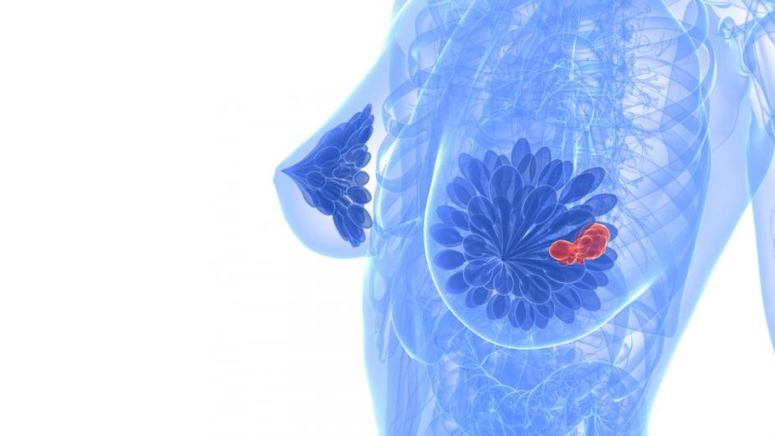
A lump in or near the breasts is one of the most common signs of breast cancer. Many breast cancer awareness leaflets recommend regular self-examination of the breasts and the areas around them. This can help in the detection of lumps that may not noticeably bulge. Breast cancer lumps are typically painless. They also tend to be hard with irregular edges [2].
If you feel a lump near your breasts while examining them, it might be indicative of breast cancer. You should see a doctor as soon as possible. While a breast lump should be taken seriously, there is often no need to panic.
Not all breast lumps are a sign of breast cancer. Most are not [3], but it is still better to confirm what your lump means. Conditions that can cause lumps to form in the breasts besides cancer include fibrocystic breast disease, fibroadenoma (noncancerous tumors), breast infection, and fat necrosis.