Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a form of psychotherapy that can be used to treat bipolar disorder. Psychotherapy [1] involves interaction with a therapist, either personally or in a group session with other people with similar issues.
Although there are many approaches to CBT, the overall aim is to help people manage their perceptions, thoughts, and behavior. Psychotherapy also helps people find healthy ways to handle certain problems.
How does CBT fit into treatment?
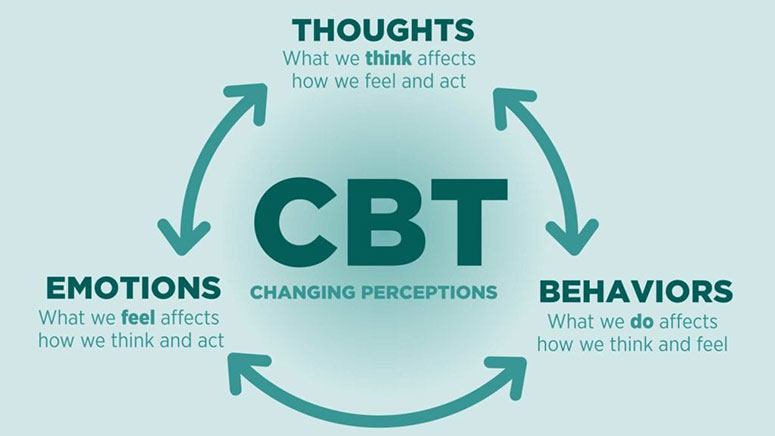
The major treatment approach for bipolar disorder is a combination of medication and psychotherapy. Cognitive behavioral therapy is one of the more common types of psychotherapy.
CBT helps treat bipolar disorder by:
- Addressing the feeling of guilt or other negative thoughts and beliefs about manic episodes
- It also helps tackle depressive symptoms that occur as part of periods or episodes of depression [2]
- Addressing the feeling of losing friends or relationships
Overall, CBT can help reduce distress and manic or depressive episodes. It can also help create awareness of one’s mood, physical sensation, emotions, and common indicators of a manic episode.
This awareness can prepare one for manic episodes and help treat them better by:
- Engaging in behaviors that help relieve your condition, such as sleeping and proper self-care
- Booking regular appointments with your psychiatrist [3]
- Make practical plans to prevent risks associated with bipolar disorder, such as having a trusted friend to help handle your spending if you have a history of spending behaviors.
Some of the ways CBT can be used include:
- To manage certain symptoms of mental health conditions
- To prevent behaviors that can be harmful to one’s health
- To master effective coping techniques that can help control emotions and stress
- It may also serve as an alternative treatment until a good regimen of medications is found













