What is Hodgkin Lymphoma?
Hodgkin lymphoma (also called Hodgkin’s disease) is a type of cancer that begins in specific kinds of white blood cells called lymphocytes. These white blood cells are present in the lymph, a clear fluid that plays a critical role in the body’s immune defense system and helps control the flow of body fluids.
There are two types of lymphomas: Hodgkin lymphoma is one and Non-Hodgkin lymphoma is the other. Both types of lymphomas behave and proliferate differently. The methods for treating them also differ, so it is important to be sure which type you have.
In the lymph system where Hodgkin lymphoma starts, there are two main types of lymphocytes: B lymphocytes and T lymphocytes. B lymphocytes (B cells) produce antibodies that help shield the body from the attack of bacteria and viruses. T lymphocytes (T cells) are of many types. Some help the immune system destroy harmful foreign invaders and abnormal cells in the body. Others help regulate the activity of other cells in the immune system.
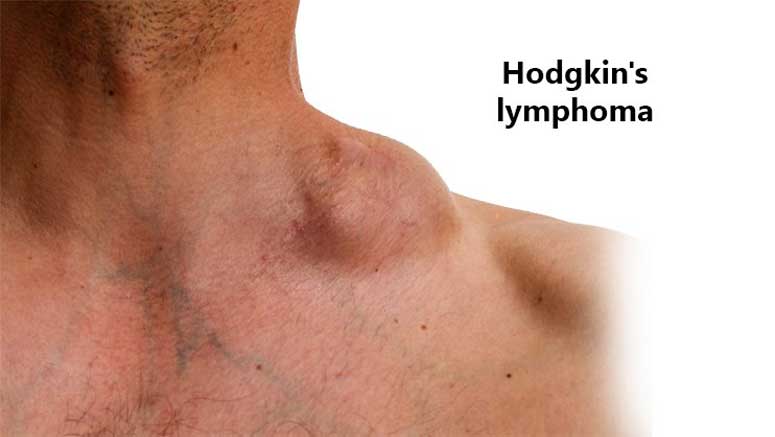
Hodgkin lymphoma often begins in the B lymphocytes [1]. Hodgkin’s disease, more often than not, begins in the lymph nodes in the upper body (neck, chest, or armpits). It spreads to the lymph vessels from these lymph nodes.
In severe cases of late-stage Hodgkin lymphoma, the cancer can spread into the bloodstream and affect organs such as the lungs, liver, and bone marrow.











