Diagnosis
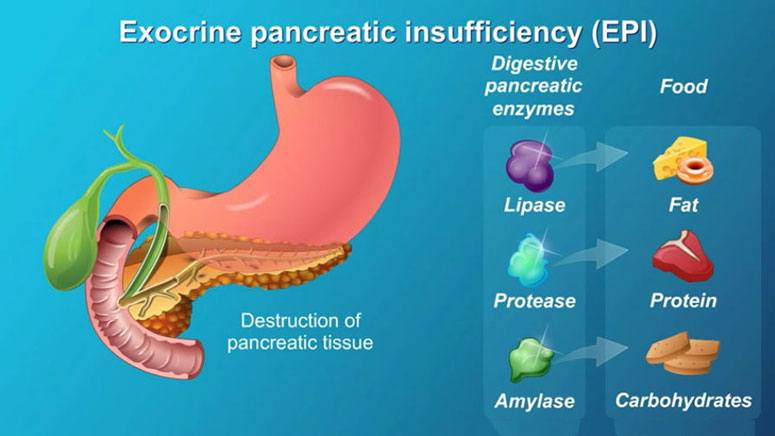
A person with EPI is usually unable to digest fats, proteins, and carbohydrates in his/her diet. In addition to preventing adequate digestion, EPI causes some uncomfortable gastrointestinal symptoms.
Do not panic if you have some mild indigestion, it might not be EPI. Only your doctor can confirm if you have this medical condition.
Visit your doctor if you have recurrent indigestion and explain your symptoms. Ensure you open up about all your symptoms and don’t hide anything. Even the littlest piece of information is important in confirming a diagnosis.
Some questions your doctor may ask include;
- Do you experience pain in your abdomen?
- Have you lost excess weight over a short period?
- Do you have gas?
- Is your poo fowl smelling or hard to flush?
You may need to conduct several tests to help diagnose EPI. These tests include;
- A blood test: a blood test will be required to check if you are getting enough vitamins. It can also help to detect celiac disease, which can cause EPI.
- 3-day faecal test: this test checks for the amount of fat in your stool. To do this, you will be required to collect samples of your stool in special bottles for 3 days.
- Faecal elastase-1: this test is used to detect if the pancreas is producing enough of an important enzyme needed for digestion. You will also be required to collect a sample of your poo into a container and send it to the lab.
- Secretin pancreatic function test: this test is done to check how the pancreas responds to secretin. To carry out this test, secretin [2] is passed through an intravenous (IV) line, an endoscopic ultrasound is then used to collect fluid from the digestive tract. It is then taken to the lab to test for the enzymes present in the pancreatic juice.
Some other tests to confirm if the pancreas is inflamed include;
- CT scan
- MRI
- Endoscopic Ultrasound [3]













