Rheumatoid arthritis
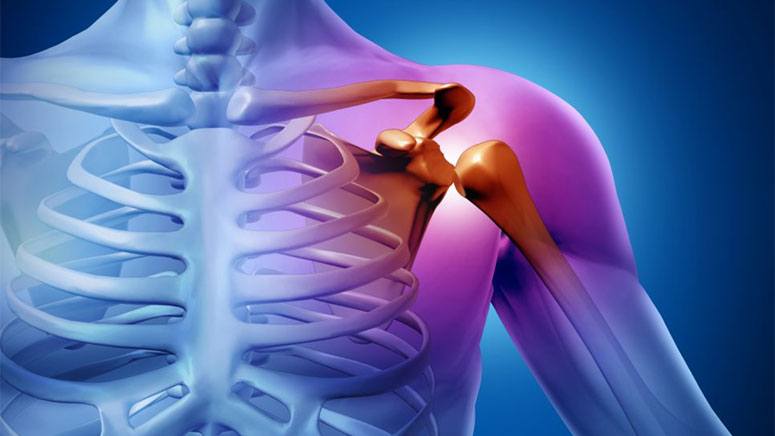
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA), the second most common type of arthritis to impact the shoulder joint, is an autoimmune and inflammatory disease. RA is a condition that causes one’s immune system to attack the very cells they are supposed to defend, causing chronic inflammation in the affected tissues.
In RA, your immune system attacks your synovial tissues [3], which make up the thin membranes that lubricate your joints to help make joint movement easier and more fluid. As RA attacks this lining and causes it to swell, the affected joint may feel stiff, painful, swollen, and hard to move.
RA is a chronic disease that is not only particular to the shoulder joints. It’s also a symmetrical disease, meaning that if it affects one of your shoulders, it’s likely to affect the other one, too.
The disease can happen to anyone no matter the age or gender. However, its onset is most common in people in their 60s.













