What Is Osteoporosis and the Symptoms?
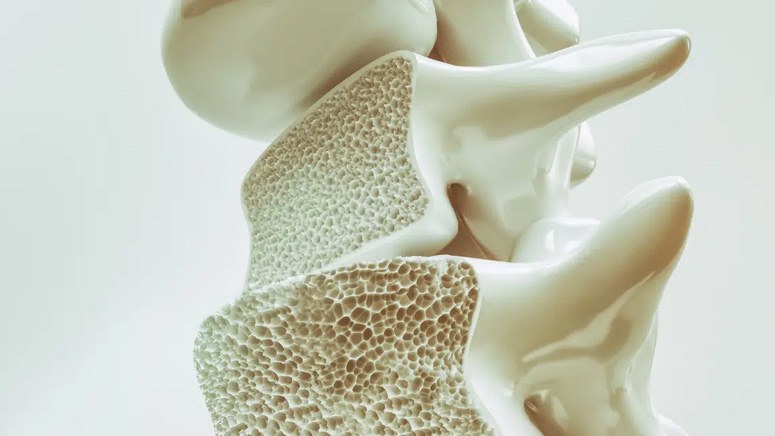
Osteoporosis is a bone disease that occurs when your bone mass and bone mineral density reduces. It is also caused by different alterations in the structure and quality of your bone. This disease can reduce the strength of a bone and make it more susceptible to risk fractures [5]. The interior portion of a bone has similar structural spaces as a honeycomb structure. Osteoporosis increases these spaces, and as a result, weakens the bone.
According to research, the leading cause of osteoporosis is age. In people older than 45, the body’s ability to break down bones is faster than its ability to replace it. This makes the bones weaker and more susceptible to fracture. Menopause also plays a significant role in causing osteoporosis, because increase or decrease in hormone levels can lead to bone loss.
Other factors responsible for causing osteoporosis include:
- Small body frame
- Smoking
- Low body weight
- Family history of osteoporosis
- Poor nutrition
Studies show that women are more susceptible to osteoporosis than men. Asian and white women are more prone to the condition.
In the early stages of osteoporosis, there are usually no symptoms. For this reason, it is usually referred to as a “silent” disease. In most cases, you may not know you have the condition until your vertebrae are affected or your bone breaks. One of the most common symptoms of a broken or collapsed vertebrae is chronic pain and hunched posture. Osteoporosis makes bones prone to collapsing or breaking after a minor fall or normal stressors such as coughing or lifting.













