Streptococci and Staph
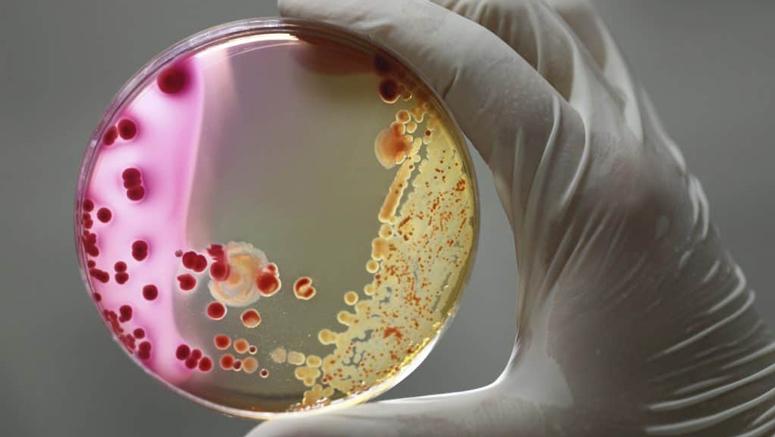
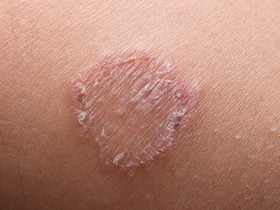
The most popular bacteria that is responsible for cellulitis are beta-hemolytic streptococci (groups A, B, C, G and F). A type of superficial cellulitis caused by strep is called erysipelas and is characterized by spreading hot, bright red circumscribed area on the skin with a sharp elevated border. Erysipelas is more popular in young children.
They are referred to as “flesh-eating bacteria” that can destroy tissues in deep locations under the skin. Fasciitis is also used to refer to inflammation of the very deep lining tissues called fascia. The streptococcal infection is also called flesh-eating bacterial infection and is an example of fasciitis. If cellulitis is not treated properly, it can spread to the deeper tissues and cause severe serious fasciitis [1].
Staph (staphylococcus aureus), including methicillin-resistant strains (MRSA), is another popular kind of bacteria that causes cellulitis. Methilin-resistant S aureus (MRSA) has caused an increased occurrence of community-acquired infections, which is a very dangerous type of staph infection that cannot be treated by antibiotics such as methicillin [2] and as a result it is hard to manage.