Arteriosclerosis is also referred to as cardiovascular arteriosclerosis, which is a heart condition that occurs when the arteries (vessels that carry blood away from the heart) grow stiff and thick, thereby restricting blood flow to vital organs and tissues in the body.
Healthy arteries are elastic and flexible, but as time goes on, walls of the arteries can harden. This is a gradual process also referred to as hardening of the arteries, which weakens arteries and can develop in different organs, but most often in the heart.
Arteriosclerosis can develop into atherosclerosis, which can lead to heart disease like stroke, circulation issues in the legs and arms, chronic kidney disease, aneurysms that can cause life-threatening internal bleeding.
Atherosclerosis is a specific type of arteriosclerosis, [1] but these two terms are used interchangeably to mean the same thing, given the fact that both of them lead to a decrease in blood flow to other parts of the body. Atherosclerosis is the buildup of cholesterol, fats, calcium, and other substances in and on your arteries walls. As they build up, the arteries become hard and narrow.
This buildup is referred to as plaque, this plaque can cause your arteries to narrow and block your blood flow. It could also burst to lead to a blood clot, which can prevent the blood flow to a specific part of the body, such as when blocked blood flow to the heart causes a heart attack.
A blood clot can also travel to other parts of your body, blocking flow to another organ.
Atherosclerosis may start as early as in childhood, and it gets worse over time. Hardening of the blood arteries can lead to various problems as narrowed/ blocked arteries can’t deliver enough blood, oxygen, and nutrients to other parts of the body. This blockage might eventually cause tissue death or infection in the arms, legs, or any other part of the body.
Though considered to be a heart problem, atherosclerosis can affect any arteries in any organ of the body.
There are 3 main types of arteriosclerosis, which include;
- Atherosclerosis: Hardening and narrowing of large arteries.
- Moenckeberg Medial Calcific Sclerosis: This is the hardening of small to medium-sized arteries.
- Arteriolosclerosis: This is the calcification (the process whereby calcium builds up in body tissue causing them to harden) of small arteries.
Signs & Symptoms
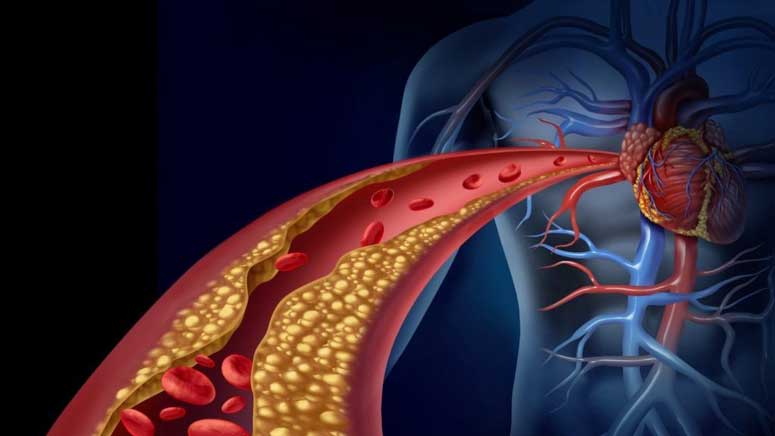
Mild atherosclerosis/arteriosclerosis won’t have symptoms unless an artery is so narrow or heavily clogged to the point that it can’t supply enough blood to organs and tissues. Most times a blood clot blocks off blood flow, or even breaks apart and can trigger a heart attack or stroke.
The signs and symptoms of arteriosclerosis depend on the type of vessel affected by the disease.
- If the affected vessels are the cerebral or ophthalmic vessels (as in cerebrovascular accidents or transient ischemic attacks) symptoms and signs may include; facial or lower limb numbness, confusion, sudden weakness, difficulty understanding speech, and seeing problems. These signals, if left untreated, may lead to a stroke.
- If you have atherosclerosis in the arteries leading to the kidneys, you develop high blood pressure or kidney failure.
- If you have atherosclerosis in the arteries in your arms and legs, you may develop signs of peripheral artery disease, such as leg pain when walking (claudication) or decreased blood pressure in the affected limb.
- If you have atherosclerosis in the heart arteries, you may develop symptoms such as chest pain or pressure (angina).
As the condition worsens into atherosclerosis, mild cases may still not show symptoms which is why regular checkups are important. As arteriosclerosis progresses, clogged arteries can trigger a heart attack [2] or stroke with symptoms which include;
- Slurred speech or difficulty
- Chest pain or pressure
- Brief loss of vision in one eye
- Drooping facial muscles
- Pain when walking
- High blood pressure
- Kidney failure
- Sudden arm or leg numbness or weakness
- Arrhythmia (an unusual heartbeat)
- Shortness of breath
- Paralysis
- Severe headache
The symptoms of arteriosclerosis may look like other heart conditions but can be diagnosed in the following ways:
- Cardiac Catheterization
- Doppler sonography
- Blood pressure comparison
- MUGA/radionuclide angiography
- Thallium/myocardial perfusion scan
- Computerized tomography or CT













