Overview
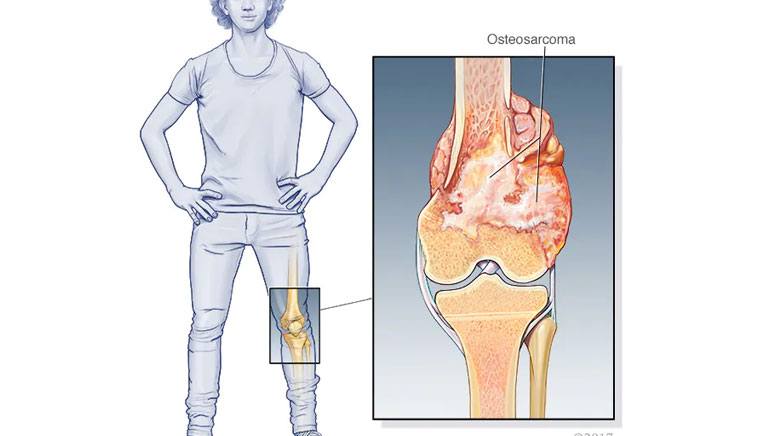
Osteosarcoma, also known as osteogenic sarcoma, is a form of cancer that develops in the bones. At first, the cancer cells resemble normal bone cells. Tumours are then produced, and those tumours result in the formation of immature, irregular, and diseased bone. With a 15-year-old median diagnosis age, osteosarcoma is most frequently found in teenagers.
The term “sarcoma” refers to a specific kind of cancer that appears in connective tissue like bone, cartilage, or muscle. The word “osteo” means “bones.”
Long bones like those in the arms and legs are the ones that osteosarcoma most frequently affects. If you’re a teenager, it typically happens where the fastest growth is occurring, which is near your knee and the metaphyses at the ends of your bones. The bones and regions that are most frequently impacted include:
- Femur (thigh bone) near your knee.
- Tibia (shin bone) near your knee.
- Humerus (upper arm bone) near your shoulder.
- Rarely, in the soft tissues or organs in your abdomen or chest.
Other less common locations for osteosarcoma include your:
- Pelvis.
- Jaw
- Skull.