Overview

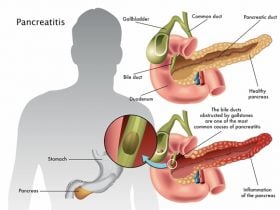
Amyloidosis [1] is a serious health problem caused by the unusual build-up of a type of protein in the body’s tissues and organs. This protein, called amyloid, changes the shape of these organs and alters their normal function. Amyloidosis can result in various health complications including organ failure and should be addressed with urgency when discovered.
The build-up of amyloids in the body has been linked to different types of proteins. The type of amyloidosis a person has depends on two main things: the type of proteins that result in the amyloid build-up and the location of the build-up. Amyloids may collect in organs and tissues throughout the body or be limited to a specific site.
Amyloidosis typically affects the kidneys, heart, nervous system, spleen and digestive system. There is usually no symptom at first, so it can be difficult to spot. Even when these symptoms start to show, they can be misread since they often resemble other medical conditions.
Anyone can develop amyloidosis, but certain people are at more risk of developing it. The most common type of amyloidosis, AL amyloidosis, is more likely to occur in people between the age of 60 and 70. Almost 70 percent [2] of this type of amyloidosis happens in men. A family history of amyloidosis also increases your chances of developing the disease. People of African heritage [3] are more likely to be carriers of a genetic mutation associated with the types of amyloidosis that target the heart. People who have chronic inflammatory disease or infections are at a higher risk of AA amyloidosis which targets the liver. Being on dialysis [4] for kidney disease also predisposes one to amyloidosis.
Sadly, there is no cure for this disease yet. Finding it on time and managing it properly can reduce the chances of the condition getting worse. If you’re wondering if you have amyloidosis, see this list of early warning signs. You should see a doctor for a proper diagnosis if you’re experiencing any of them.