Esophageal cancer is cancer that is present anywhere in the esophagus (gullet or food pipe). Its complication depends on location in the esophagus and if it affects regular activities of the body. Esophageal cancer is linked to tobacco, obesity, and alcohol consumption. It Is common in men than women. The most popular types of esophageal cancer are adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. These two types of esophageal cancer can grow in different places and are controlled by various genetic changes.
The most prominent symptoms of esophageal cancer are associated with problems linked to eating, swallowing, digestion and drinking. It mostly doesn’t show signs until an advanced stage. It is essential to receive an accurate diagnosis from a medical doctor.
Trouble Swallowing
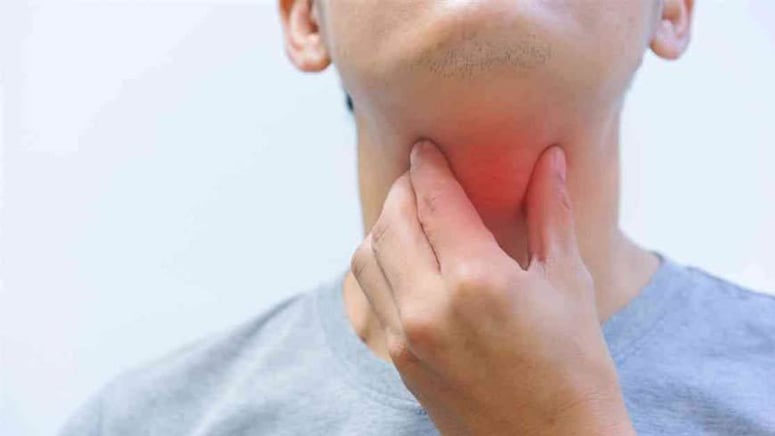
The most widespread symptom of esophageal cancer is difficulties swallowing. The patient feels like food is stuck in the throat and cannot move further downward in the digestive tract. Sometimes, the food gets into the airway, and choking is experienced. The patient finds it more difficult to swallow with time, and a doctor’s attention is needed immediately. Changing habits to avoid trouble swallowing, such as eating smaller bites, avoiding solid food, and eating softer food, can increase the risk of difficulty swallowing. The esophagus begins to narrow because of the cancer growing. Swallowing problems are usually prominent when ingesting a large bolus of food (meat, yam, and bread).













